
Verizon 5G coverage map is still not as big as T-Mobile’s; however, it is expanding its 5G coverage to more than one thousand cities and more than thirty million households. The company has already rolled out 5G Ultra Wideband service to several cities, including Omaha, NE, and Sioux Falls, SD. Its next expansion will include parts of Baltimore, MD, and Boise, ID. Its goal is to cover more than one hundred million people with 5G Ultra Wideband service by the end of 2023.
Verizon’s 5G Home Internet service is available in over twenty-five major metropolitan areas and five of the country’s most densely populated cities. The network provides average download speeds of 300 megabits per second and upload speeds of up to 200 Mbps. However, your Internet connection speed may vary depending on the location of the Verizon towers in your area.
Where is Verizon 5G actually available?
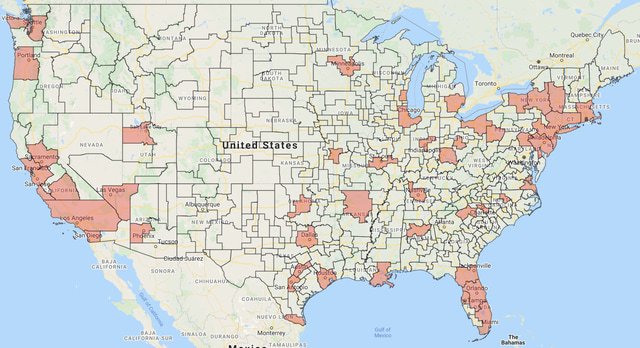
Several carriers have recently begun deploying their 5G networks across the U.S., including T-Mobile and Verizon. However, both carriers have different priorities and focus on different areas of the country. In order to decide which carrier is best for you, you should first consider where your city is likely to have 5G coverage.
Verizon’s network is currently available in 230 million households across 2,700 cities. However, it’s only widely available in population centers. This means that there are some cities where you won’t be able to use 5G, even if you live there. Here’s what you can expect from Verizon’s 5G network.
There are two different types of spectrum used for Verizon’s 5G service. The first is mmWave or mid-band spectrum. It’s more likely to have coverage outside of a city, and it’s also more consistent. Unlike the sub-6 band spectrum, mmWave signals don’t travel too far and are prone to interference.
The other type of spectrum used by Verizon is the C-band spectrum. It’s a mid-band band, and it offers much faster speeds than 4G LTE. However, it’s less widely available than mmWave.
Why is Verizon’s 5G Slow?

Using Verizon’s 5G can be a good thing, but your connection may be a bit slow. This can be caused by a number of different things, including overage on your data limit, outages on the Verizon network, or the device you’re using. Identifying these problems can help you to fix your slow Verizon connection.
The Verizon 5G network is the company’s latest mobile technology and promises to deliver blazing-fast speeds. Unfortunately, the company has yet to say how it’s going to reach 5G everywhere. It needs to be clarified whether it’s using the same spectrum as its 4G network or using a separate network system.
Verizon’s 5G network uses Dynamic Spectrum Sharing or DSS. The technology allows Verizon to reuse part of its 4G network for 5G. The problem is that the DSS 5G is often slower than 4G, which means you’ll only get a faster 5G when you’re near an ultra-wideband 5G network.
One of the most impressive features of the Verizon 5G network is its ability to deliver ultra-low latency. This technology allows for augmented reality and gives customers more information faster.




